Signals and slots is a language construct introduced in Qt for communication between objects[1] which makes it easy to implement the observer pattern while avoiding boilerplate code. The concept is that GUI widgets can send signals containing event information which can be received by other widgets / controls using special functions known as slots. This is similar to C/C++ function pointers, but signal/slot system ensures the type-correctness of callback arguments.[citation needed]
Dec 29, 2012 Let's say I have a signal change connected to a slot notify. If the change signal is emitted, the notify slot will start executing. Now what happens if a second change signal is emitted and the first notify slot didn't finish its execution? Is the second slot launched concurrently with the first? And if so, is Qt handling the thread-safety. Qt is well known for its signals and slots mechanism. But how does it work? In this blog post, we will explore the internals of QObject and QMetaObject and discover how signals and slot work under the hood. In this blog article, I show portions of Qt5 code, sometimes edited for formatting and brevity. Sep 08, 2015 lsignal (or lightweight signal) is a very little and fast C thread-safe implementation of signal and slot system which is based on modern C11 code.
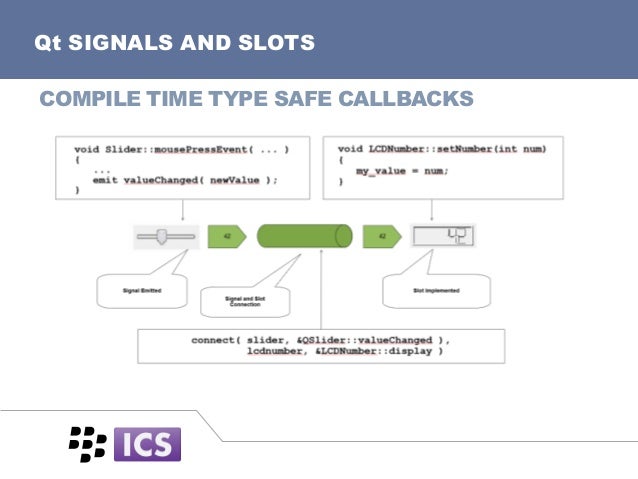
The signal/slot system fits well with the way graphical user interfaces are designed. Similarly, the signal/slot system can be used for other non-GUI usages, for example asynchronous I/O (including sockets, pipes, serial devices, etc.) event notification or to associate timeout events with appropriate object instances and methods or functions. It is easy to use and no registration/deregistration/invocation code need to be written, because Qt's metaobject compiler (MOC) automatically generates the needed infrastructure.
A commonly used metaphor is a spreadsheet. A spreadsheet has cells that observe the source cell(s). When the source cell is changed, the dependent cells are updated from the event.
Alternative implementations[edit]

There are some implementations of signal/slot systems based on C++ templates, which don't require the extra metaobject compiler, as used by Qt, such as libsigc++, sigslot, vdk-signals, nano-signal-slot, neosigslot, Signals, boost.signals2, Synapse, Cpp::Events, Platinum and JBroadcaster. Common Language Infrastructure (CLI) languages such as C# also supports a similar construct although with a different terminology and syntax: events play the role of signals, and delegates are the slots. Another implementation of signals exists for ActionScript 3.0, inspired by C# events and signals/slots in Qt. Additionally, a delegate can be a local variable, much like a function pointer, while a slot in Qt must be a class member declared as such. The C based GObject system also provides similar functionality via GSignal.In D it is implemented by std.signals.
See also[edit]
Libraries[edit]
Java: sig4j - multi-threaded, type-safe, based on the FunctionalInterface annotation introduced in Java 8.
C++: vdk-signals - thread-safe, type-safe, written in C++11 with atomic variables.
Signal Slot Thread Safety

References[edit]
Pyside2 Signal Slot
- ^'Signals & Slots - QtCore 5.1'. Qt Project. 2013-07-04. Retrieved 2013-07-04.
Comments are closed.